Project Overview
COVID-19 global pandemic affects health care and lifestyle worldwide, and its early detection is critical to control cases’ spreading and mortality. The actual leader diagnosis test is the Reverse transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), result times and cost of these tests are high, so other fast and accessible diagnostic tools are needed. Inspired by recent research that correlates the presence of COVID-19 to findings in Chest X-ray images, this project evaluates the use of deep learning models, in particular Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), to process these images and classify them as positive or negative for COVID-19, furthermore to develop a Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) tool for the disease.
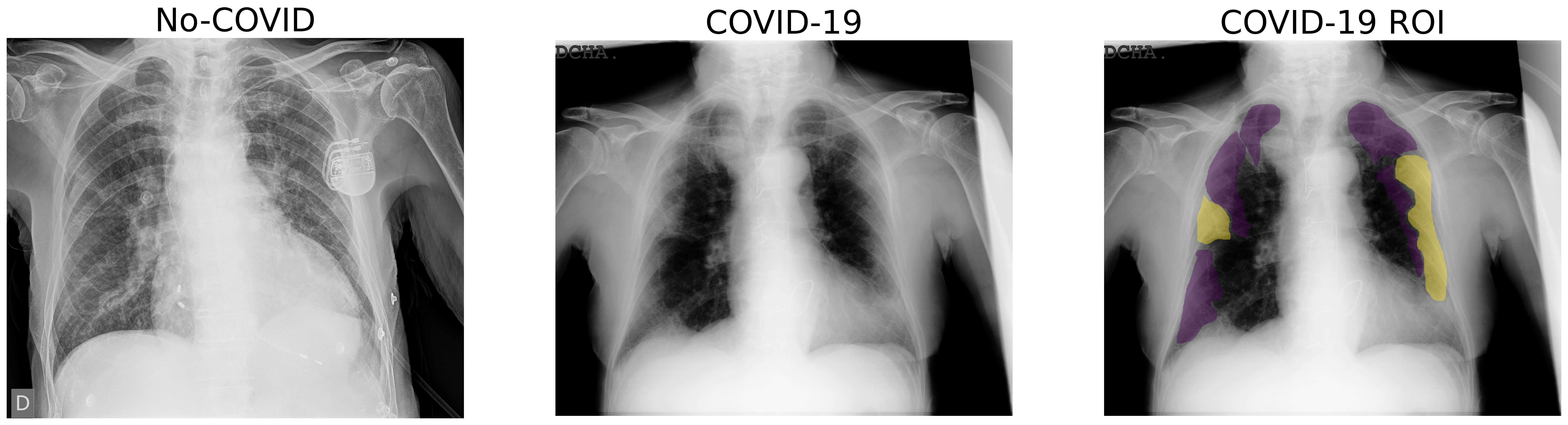
The possibility of applying semantic segmentation or object localization to find the regions of the image associated to COVID-19 presence, called Ground Glass Opacities (GGO) by radiologists, it is also being explored.
Results Highlight
Results presented in this section correspond to experiments performed in [1] using transfer learning on VGG16 and VGG19 networks. Specifically, the accuracies presented were achieved using lung segmentation to force the model to extract information from the relevant areas for the task. For more information refer to the scientific paper linked below.
| Model | Train | Validation | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 0.9958 | 0.9376 | 0.9299 |
| VGG19 | 0.9937 | 0.9449 | 0.9363 |
Products
[1] D. Arias-Garzón et al., “COVID-19 detection in X-ray images using convolutional neural networks,” Mach. Learn. with Appl., vol. 6, p. 100138, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100138.